Visual memory plays a critical role in a child’s cognitive development, significantly influencing their academic and everyday life skills. It is the ability to remember and recall information that has been seen. Children with strong visual memory can recall shapes, colors, patterns, and sequences, which is vital for reading, writing, and mathematics. From recognizing the face of a loved one to remembering the route to school, visual memory aids children in interpreting and making sense of the world around them. But how can we enhance this critical skill? In this article, we delve into practical ways of developing visual memory in children, with a specific focus on those aged between 3 and 6 years. We’ll also discuss its significance in the context of their broader learning journey.
Visual memory refers to one’s ability to remember and recall visual information. It encompasses an array of skills, including the recall of colors, shapes, symbols, images, patterns, and sequences. According to the Child Development Institute, visual memory is a key predictor of academic success, playing a pivotal role in areas such as reading, spelling, mathematics, and problem-solving. Moreover, visual memory supports a range of everyday activities, from remembering faces to navigating the environment. In short, it’s a foundational cognitive ability that significantly influences a child’s learning trajectory and day-to-day functioning. Ensuring its development from an early age is thus crucial.
Developing visual memory in children need not be a daunting task. Here are some fun and engaging activities that can aid in enhancing this important skill:
Remember, the key is to make the learning process enjoyable and pressure-free. The more fun children have while playing these games, the more they’ll engage with the task, enhancing their visual memory skills.
Teaching visual memory to children can be both fun and engaging, especially with the right resources at your disposal. Smart Tales offers a plethora of interactive stories, educational games, and enlightening worksheets geared towards enhancing a child’s visual memory. These tools are thoughtfully designed, taking into account the cognitive capabilities and interests of preschool children aged between 3 and 6. Read on to find out how to leverage these resources to stimulate your child’s visual memory and pave the way for their academic success.
Smart Tales hosts a variety of stories designed to hone visual memory skills in children. These tales, imbued with rich imagery and vivid characters, encourage children to remember visual cues and sequences, thereby fortifying their visual memory. So, let your little one dive into the enchanting world of Smart Tales and discover the power of their memory.
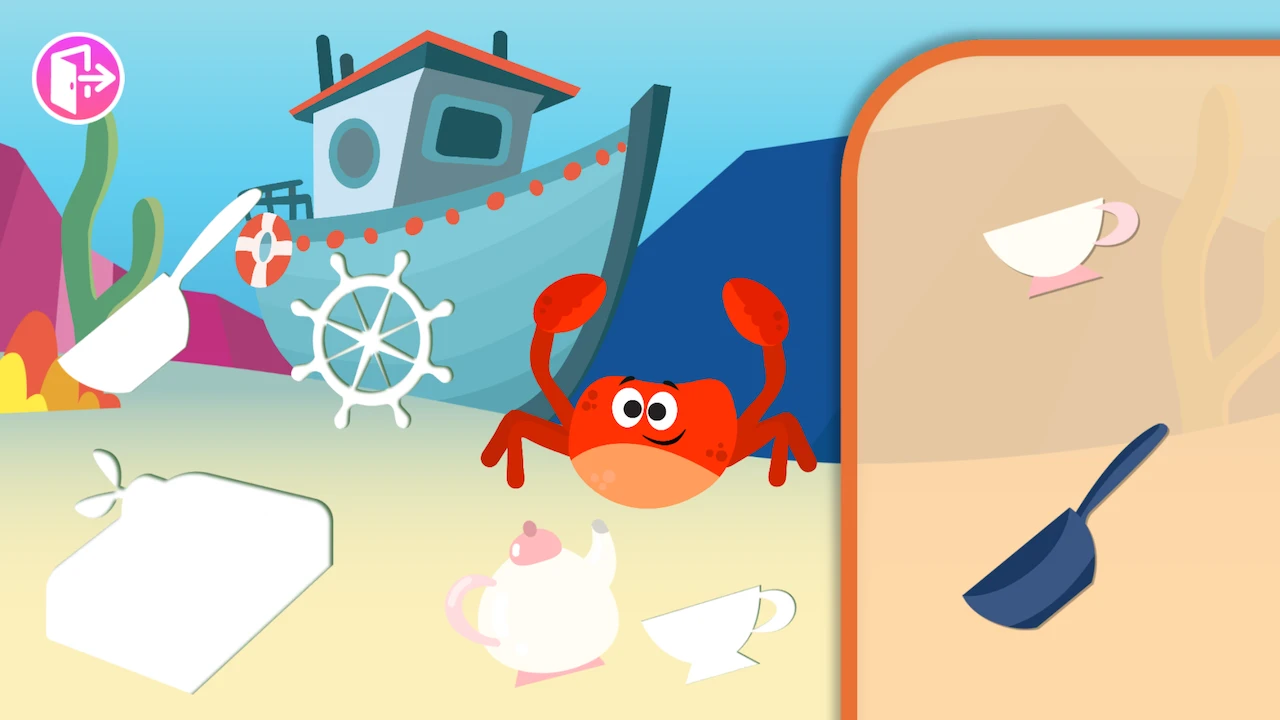
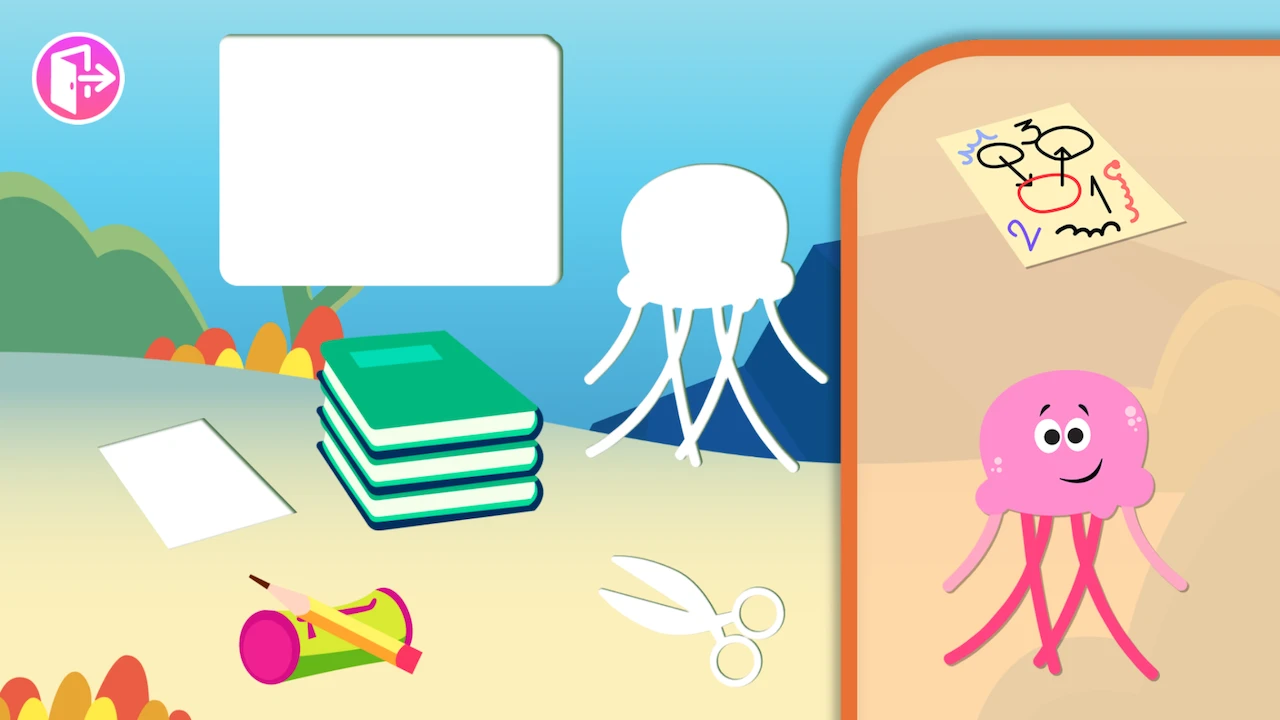
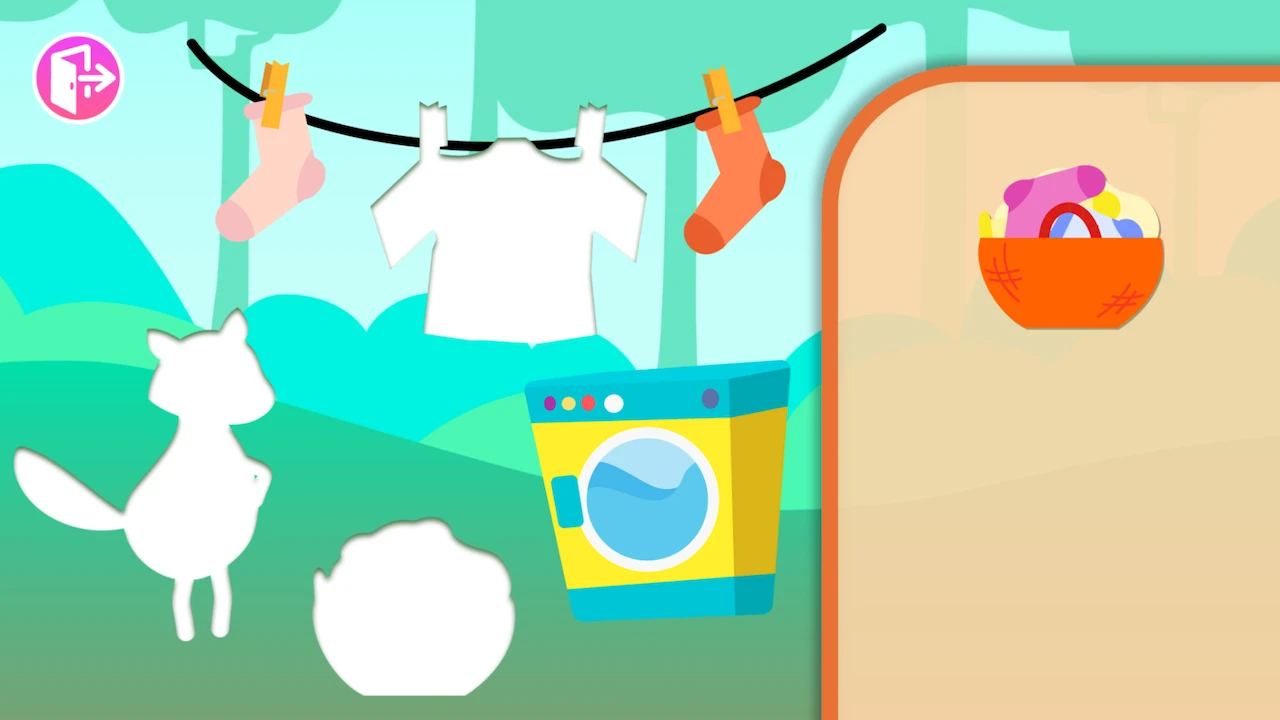
Enhance your child’s visual memory through fun-filled and educational games offered by Smart Tales. These games, tailored for children aged 3 to 6, encourage them to memorize visual patterns and recall them, offering a fun and effective way to strengthen visual memory. Explore these games today and watch your child’s visual memory skills soar!
Augment your child’s learning journey with Smart Tales’ educational worksheets aimed at boosting visual memory. These worksheets, designed by educational experts, engage children in stimulating activities, encouraging them to visually memorize and recall shapes, symbols, and patterns. Start using these worksheets and make learning a visually rewarding experience!
In conclusion, developing a child’s visual memory from an early age is of paramount importance, as it greatly contributes to their academic achievement and overall cognitive development. By integrating strategies like memory games, storytelling, and educational worksheets, all of which are abundantly available on Smart Tales, parents and teachers can effectively and enjoyably strengthen a child’s visual memory. In so doing, they equip children with a vital skill that aids them in their learning journey and beyond. Explore the wonderful world of Smart Tales and help your child unlock the full potential of their visual memory.